西安科技大学机械工程学院,陕西 西安 710054
高速激光熔覆过程中的温度变化和扫描路径位置变换均对涂层组织与性能有较大影响。利用高速激光熔覆技术在27SiMn钢表面以回字形扫描路径制备了铁基TY-1涂层,对比分析了同一参数下回字形路径上的温度变化对涂层组织和性能的影响。利用ANSYS Workbench有限元分析软件模拟了高速激光熔覆过程,获得了回字形路径上不同位置处涂层的温度场分布规律,并通过微观组织和性能分析实验进一步分析了温度变化对涂层组织和性能的影响。结果表明:回字形扫描路径下由中心点向外的熔池最高温度分别为1890、1955、1998 ℃;不同位置处的涂层间温度相互影响,相较于回字形内部(距中心点1~19 mm)和中部(距中心点19~34 mm)处的涂层,外部(距中心点34~46 mm)涂层熔覆完成后在空气中冷却,没有后续熔覆道次对其施加温度上的影响,冷却速率相对较快,因而晶粒组织分布均匀,硬度和耐蚀性均较高。
激光技术 高速激光熔覆 温度场 微观组织 显微硬度 耐蚀性
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Precision and Non-Traditional Machining
2 University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE 68588, United States of America
International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2019, 1(2): 020201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
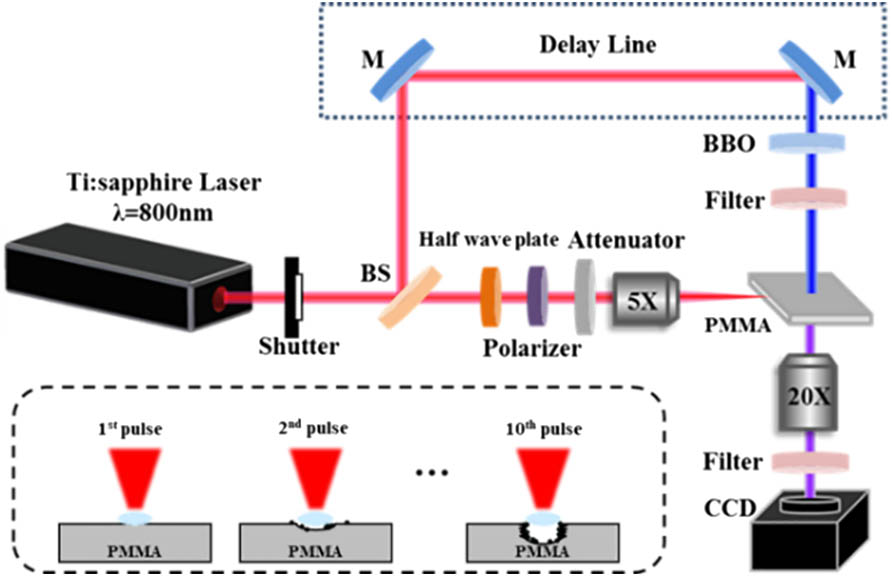
Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7120 Ultrafast phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 350.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Laser Thermal Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
The dynamics of plasma and shockwave expansion during two femtosecond laser pulse ablation of fused silica are studied using a time-resolved shadowgraph imaging technique. The experimental results reveal that during the second pulse irradiation on the crater induced by the first pulse, the expansion of the plasma and shockwave is enhanced in the longitudinal direction. The plasma model and Fresnel diffraction theory are combined to calculate the laser intensity distribution by considering the change in surface morphology and transient material properties. The theoretical results show that after the free electron density induced by the rising edge of the pulse reaches the critical density, the originally transparent surface is transformed into a transient high-reflectivity surface (metallic state). Thus, the crater with a concave-lens-like morphology can tremendously reflect and refocus the latter part of the laser pulse, leading to a strong laser field with an intensity even higher than the incident intensity. This strong refocused laser pulse results in a stronger laser-induced air breakdown and enhances the subsequent expansion of the plasma and shockwave. In addition, similar shadowgraphs are also recorded in the single-pulse ablation of a concave microlens, providing experimental evidence for the enhancement mechanism.
(320.7100) Ultrafast measurements (140.3390) Laser materials processing (140.3440) Laser-induced breakdown. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000488
1 华中科技大学武汉光电国家实验室, 湖北 武汉 430074
2 美国内布拉斯加林肯大学电子工程系, 林肯 68503, 美国
3 北京理工大学机械与车辆学院, 北京 100081
介绍了碳纳米管(CNTs)/聚合物复合材料分散性、定向排布和组装方面的研究进展, 并利用双光子聚合(TPP)激光直写技术, 实现了多壁碳纳米管(MWNTs)在三维空间的定向排布和分子组装。通过加入硫醇分子, 提升了MWNTs/聚合物复合材料中CNTs的分散性和掺杂浓度, 增强了CNTs/聚合物复合材料在电学、光学、力学方面的性能, 并成功实现了三维CNTs功能器件的制造。研究结果表明, 通过将TPP激光直写技术与热退火工艺相结合, 可以实现对CNTs簇排列方向和位置的精确控制。
激光制造 三维微纳制造 碳纳米管 双光子聚合 飞秒激光直写

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano-Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~52. The phenomenon is attributed to the uniform energy distribution in the long propagation distance, which leads to the long and uniform laser-modified regions and subsequent HF acid etching of laser-modified regions with high selectivity. This method will have potential applications in fabrication of HAR microgrooves in transparent materials.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication 320.5540 Pulse shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588-0511, USA
A surprising phenomenon can be discovered by using femtosecond double-pulse ablation of silicon and germanium in ethanol. The ablation areas present an oscillation increase phenomenon when the pulse delay increases from 200 fs to 1 ps in the fluence range of 0.5–0.6 J/cm2. In contrast, the ablation areas exhibit an oscillation decrease phenomenon as the pulse delay increases when the laser fluence F<0.5 J/cm2, which is consistent with the results of the experiment in air. It is considered that the adjustment of the photon–electron coupling efficiency by pulse train technology plays an important role in the ablation process.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(4): 041402
1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln NE 68588, USA
2 Technology and Applications Center, Newport Corporation, Irvine, CA 92606, USA
3 Institute of Chemistry of Condensed Matter of Bordeaux, ICMCB-CNRS 87, Avenue du Docteur Albert Schweitzer F-33608 Pessac Cedex, France
Advanced micro/nanofabrication of functional materials and structures with various dimensions represents a key research topic in modern nanoscience and technology and becomes critically important for numerous emerging technologies such as nanoelectronics, nanophotonics and micro/nanoelectromechanical systems. This review systematically explores the non-conventional material processing approaches in fabricating nanomaterials and micro/nanostructures of various dimensions which are challenging to be fabricated via conventional approaches. Research efforts are focused on laser-based techniques for the growth and fabrication of one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) nanomaterials and micro/nanostructures. The following research topics are covered, including: 1) laser-assisted chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for highly efficient growth and integration of 1D nanomaterial of carbon nanotubes (CNTs), 2) laser direct writing (LDW) of graphene ribbons under ambient conditions, and 3) LDW of 3D micro/nanostructures via additive and subtractive processes. Comparing with the conventional fabrication methods, the laser-based methods exhibit several unique advantages in the micro/nanofabrication of advanced functional materials and structures. For the 1D CNT growth, the laser-assisted CVD process can realize both rapid material synthesis and tight control of growth location and orientation of CNTs due to the highly intense energy delivery and laser-induced optical near-field effects. For the 2D graphene synthesis and patterning, roomtemperature and open-air fabrication of large-scale graphene patterns on dielectric surface has been successfully realized by a LDW process. For the 3D micro/nanofabrication, the combination of additive two-photon polymerization (TPP) and subtractive multi-photon ablation (MPA) processes enables the fabrication of arbitrary complex 3D micro/nanostructures which are challenging for conventional fabrication methods. Considering the numerous unique advantages of laser-based techniques, the laserbased micro/nanofabrication is expected to play a more and more important role in the fabrication of advanced functional micro/nano-devices.
micro/nanofabrication micro/nanofabrication laser material interaction laser material interaction carbon nanotubes (CNTs) carbon nanotubes(CNTs) graphene graphene two-photon polymerization (TPP) two-photon polymerization (TPP) multi-photon ablation (MPA) multi-photon ablation (MPA) Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2015, 8(4): 351
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 NanoManufacturing Fundamental Research Joint Laboratory of National Science Foundation of China, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Institute of Laser Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
3 Key Laboratory of Cluster Science, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
4 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
5 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE 68588-0511, USA
We present a doping method to improve the femtosecond laser ablation rate and promote ablation selectivity. Doping transition metal ions, Co2+ or Cu2+, in silicate glass apparently change absorption spectroscopy and induce resonant absorption at wavelengths of 600 and 800 nm, respectively. Comparing with femtosecond laser processing of the same glass without doping, we find that the threshold fluence decreases and the ablation rate increases in resonant absorption in doped silicate glass. Resonant absorption effectively increases multiphoton ionization for seed-free electron generation, which in turn enhances avalanche ionization.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 220.4610 Optical fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 121402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The manipulation of the subpulse number, pulse delay, and pulse energy distribution of an ultrafast laser enables electron dynamics control by changing absorptions, excitations, ionizations, and recombinations of electrons, which can result in smaller, cleaner, and more controllable structures. This letter experimentally reveals that ablation sizes and recasts can be controlled by shaping femtosecond pulse trains to adjust transient localized electron dynamics, material properties, and corresponding phase change mechanisms.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 320.7130 Ultrafast processes in condensed matter, including semiconductors 320.5540 Pulse shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(4): 041403





